🧬 DNA - The Genetic Blueprint
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the hereditary material in all living organisms. It carries the genetic instructions used in the development, functioning, and reproduction of all known living organisms.
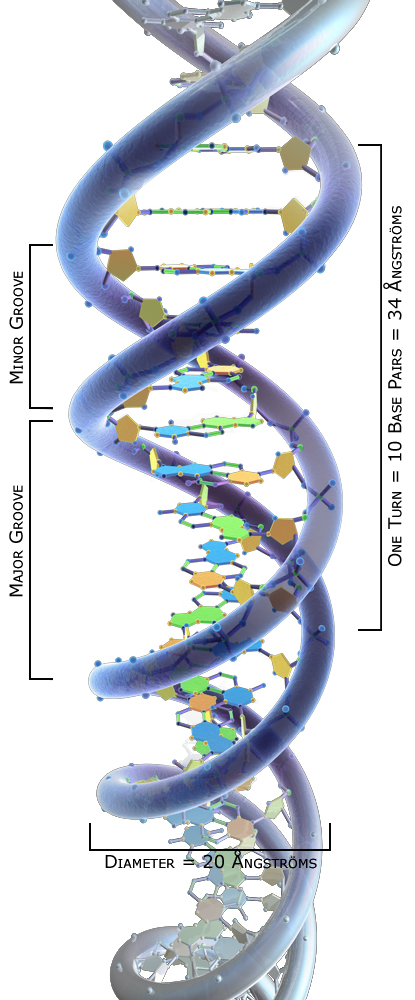
DNA Double Helix Structure
Interactive DNA Structure Visualization
• Diameter: 2 nm
• Distance between bases: 0.34 nm
• Base pairs per turn: 10
• Antiparallel strands
DNA Base Pairs
| Base Pair | Hydrogen Bonds | Type | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| A - T (Adenine - Thymine) | 2 | Purine - Pyrimidine | Weaker |
| G - C (Guanine - Cytosine) | 3 | Purine - Pyrimidine | Stronger |
PYQ Zone - DNA Structure
- The distance between two consecutive base pairs in DNA is? (NEET 2020)
- How many hydrogen bonds are present between A-T base pair? (CBSE 2018)
- What is the diameter of DNA double helix? (NEET 2019)
- Who proposed the double helix model of DNA? (CBSE 2017)
🔄 DNA Replication
DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical copies of DNA from one original DNA molecule. This process is essential for cell division and inheritance.
DNA Replication Process
Semiconservative Replication
• Leading strand (5' → 3')
• Lagging strand (Okazaki fragments)
• Helicase, Primase, DNA Polymerase
• DNA Ligase
Key Enzymes in DNA Replication
| Enzyme | Function | Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Helicase | Unwinds DNA double helix | 3' → 5' |
| DNA Primase | Synthesizes RNA primers | 5' → 3' |
| DNA Polymerase III | Main replicating enzyme | 5' → 3' |
| DNA Polymerase I | Removes primers, fills gaps | 5' → 3' |
| DNA Ligase | Joins Okazaki fragments | - |
PYQ Zone - DNA Replication
- Who proved the semiconservative nature of DNA replication? (NEET 2019)
- Which enzyme is responsible for unwinding DNA during replication? (CBSE 2018)
- What are Okazaki fragments? (NEET 2017)
- In which direction does DNA polymerase synthesize DNA? (CBSE 2019)
📝 Transcription - DNA to RNA
Transcription is the process by which genetic information in DNA is copied into RNA. It's the first step in gene expression.
Types of RNA
| RNA Type | Full Form | Function | % in Cell |
|---|---|---|---|
| mRNA | Messenger RNA | Carries genetic code from DNA to ribosomes | 5% |
| tRNA | Transfer RNA | Transfers amino acids to ribosomes | 15% |
| rRNA | Ribosomal RNA | Structural component of ribosomes | 80% |
1. Initiation: RNA polymerase binds to promoter
2. Elongation: RNA synthesis in 5' → 3' direction
3. Termination: RNA polymerase detaches at terminator sequence
PYQ Zone - Transcription
- Which enzyme is responsible for transcription in prokaryotes? (NEET 2020)
- What is the direction of RNA synthesis? (CBSE 2017)
- Which nitrogen base is found in RNA but not in DNA? (NEET 2018)
- What is the function of promoter in transcription? (CBSE 2016)
🔗 Translation - RNA to Protein
Translation is the process by which the genetic code in mRNA is decoded to produce a specific sequence of amino acids in a protein.
Genetic Code Properties
• Triplet code (3 bases = 1 codon)
• Universal (same in all organisms)
• Degenerate (multiple codons for same amino acid)
• Non-overlapping
• Comma-less (no punctuation)
| Component | Function in Translation | Location |
|---|---|---|
| mRNA | Template carrying genetic code | Ribosomes |
| tRNA | Brings amino acids to ribosomes | Cytoplasm |
| Ribosomes | Site of protein synthesis | Cytoplasm/ER |
| Amino acids | Building blocks of proteins | Cytoplasm |
1. Initiation: mRNA binds to ribosome at start codon (AUG)
2. Elongation: tRNA brings amino acids, peptide bonds form
3. Termination: Stop codon reached (UAA, UAG, UGA)
PYQ Zone - Translation
- How many codons are there in the genetic code? (NEET 2019)
- Which codon is known as the start codon? (CBSE 2018)
- What are the stop codons in genetic code? (NEET 2017)
- How many amino acids are encoded by genetic code? (CBSE 2019)
🎯 Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
The central dogma describes the flow of genetic information: DNA → RNA → Protein
Central Dogma Flow
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid
Protein
Polypeptide Chain
Replication (DNA → DNA) | Transcription (DNA → RNA) | Translation (RNA → Protein)